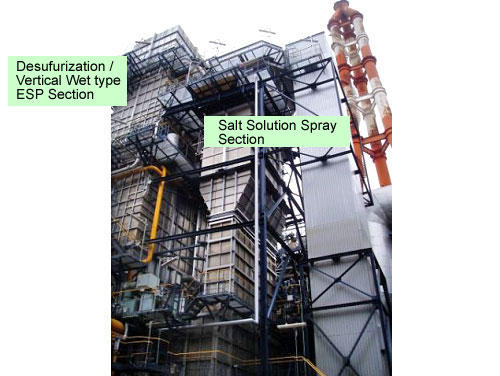
Wet System (Salt Solution Spray System + Wet type Electrostatic Precipitator)
Application of Wet type Electrostatic Precipitator (ESP)
In order to use high-sulfur fuel, it is essential to install a flue gas desulfurization system that clear SOx regulations. However, fine particles of SO3 mist slip through the desulfurization system and are discharged as bluish plume from the stack if no measures are taken. Therefore, for the purpose of collecting fine particles of SO3, one thing to do is to install a wet type electrostatic precipitator. This is another effective measure to dry treatment of SO3 (corrosion prevention and measure against bluish plume), in which an ammonia-injection system is employed.
- In a wet type ESP, dust and mist in the flue gas are collected on a liquid film formed on the collecting electrodes by electrostatic force, and washed out together with the liquid film.
- Since there is not a great deal of reentrainment of collected particles, extremely high precipitating performance is ensured, allowing for efficient collection of extremely fine particles like SO3 mist.
- Corrosion by collected SO3(H2SO4) is prevented by spraying alkaline liquid.
Details of Wet type Electrostatic Precipitator
Wet type ESPs to be installed in the stream following the desulfurization system were commercialized for practical use for the first time in the world by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and have been received favorably by customers since 1975 when the first unit for domestic use was supplied. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Power Environmental Solutions has taken over that technology. The first unit for overseas use was supplied to an oil-fired boiler in Austria in 1997. That wet type electrostatic precipitator was installed first in Europe (among local European makers) to deal with bluish plume and, at present, it is smoothly operating and enjoying a favorable reception.
Recently in Japan, the trend has been to regulate substance, and, with regulations against PM2.5 and HAPs being stringent in the USA and elsewhere overseas, the growing attention worldwide is being paid to wet type electrostatic precipitators of high performance and effective results in dealing with bluish plume.
Dissolved Salt Atomization System
This Dissolved Salt Atomization System received the President Award at the 34th Excellent Environmental Equipment Award Project in 2008 from the Japan Society of Industrial Machinery Manufacturers (sponsored by Ministry of Economy, Trade & Industry).
Outline of the System
- Recently, when heavy oil of especially high sulfur content is used as fuel, in some cases, SO3 concentration is beyond the range, which can be dealt with only with a wet type electrostatic precipitator.
- Under these circumstances, in cases where dry systems using ammonia injection system are employed, attention is given to the problem of increased disposal of mixed waste of reaction products, ammonium sulfate, and boiler dust. And, troublesome maintenance causes cost increases for dry type electrostatic precipitators.
- In order to solve these problems, a "Salt Solution Spray System", which sprays a mist of high-concentration soluble salts (Na and Mg constituents) contained in wastewater from the desulfurization system into the flue upstream of the desulfurization system, was developed as a new SO3 removing system
- The salt solution spray system, when combined with desulfurization equipment, can work as an independent SO3 removal system.
- Furthermore, according to the required performance at the stack outlet, it is practical to add a wet type electrostatic precipitator at the outlet of the desulfurization system.
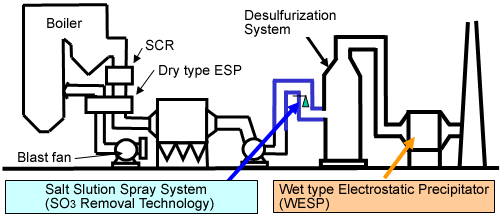
System Outline
- Soluble salts sprayed into the flue gas at upstream of the desulfurization system remove SO3 in the course of drying and solidification using waste gas heat.
- Solid salts containing SO3 (sulfuric acid), after being subjected to drying and solidification, are introduced into the desulfurization equipment and are removed from the gas through contact with a circulating liquid in the desulfurization system.
- Soluble salts (solid matters) containing removed sulfuric acid redissolve because of their solubility in the circulating absorption liquid in the desulfurization system, and the sulfuric acid is neutralized by the neutralizer in the desulfurization system.
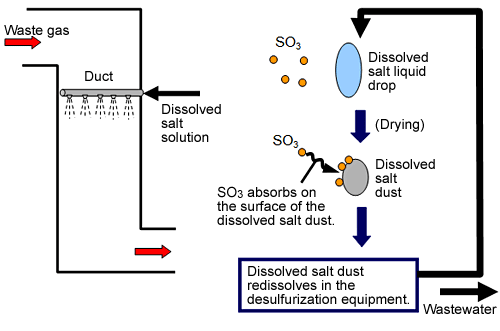
Features of the System
- Just spraying solution of high salinity as a fine mist at the inlet of desulfurization system makes high-concentration SO3, which can then be stably removed.
- Stable SO3 removal performance can be offered without being affected by the inlet SO2 concentration.
- Different from conventional NH3 injection systems, no special chemical agent is required as desulfurization wastewater (Na2SO4, MgSO4, etc) is available from sodium hydroxide process (Na-process) or magnesium hydroxide process (Mg-process).
- Since SO3 can be turned to the by-product from the desulfurization system (in the case of Na-process or Mg-process flue gas desulfurization systems, SO3, which is contained as soluble salts in the Na2SO4 and MgSO4 in the wastewater, can be discharged as effluent.), special incidental facilities for ash treatment (waste treatment in consideration of NH3) and wastewater treatment (treatment of nitrogen mixed in the desulfurization treatment wastewater), which should be considered when NH3 injection method is introduced, are not required, thus achieving a reduction in waste discharged from the system and a substantial decrease in running costs.
- Combining a wet type ESP, which is installed to control dust concentration and SO3 concentration at the stack outlet, with salt solution spray system allows for a compact wet type ESP and a substantial reduction in SO3 at the outlet.
- Simple configuration with a small number of major parts.

(without operation of salt solution spray)

(with operation of salt solution spray)
Example of actual application