Electrostatic Precipitator
Supports high capacity treatment
1.05 million kW |
Minimum dust concentration at ESP outlet
Dry type: ≤ 10 mg/m3N
|
High-resistivity dust measure
Moving electrode type
|
ESP
High reliability |
Electrostatic Precipitators (EPs) contribute to the preservation of the air environment in a wide range of fields, including thermal power plants, steel manufacturing plants, and various other industrial plants.
Principle / features
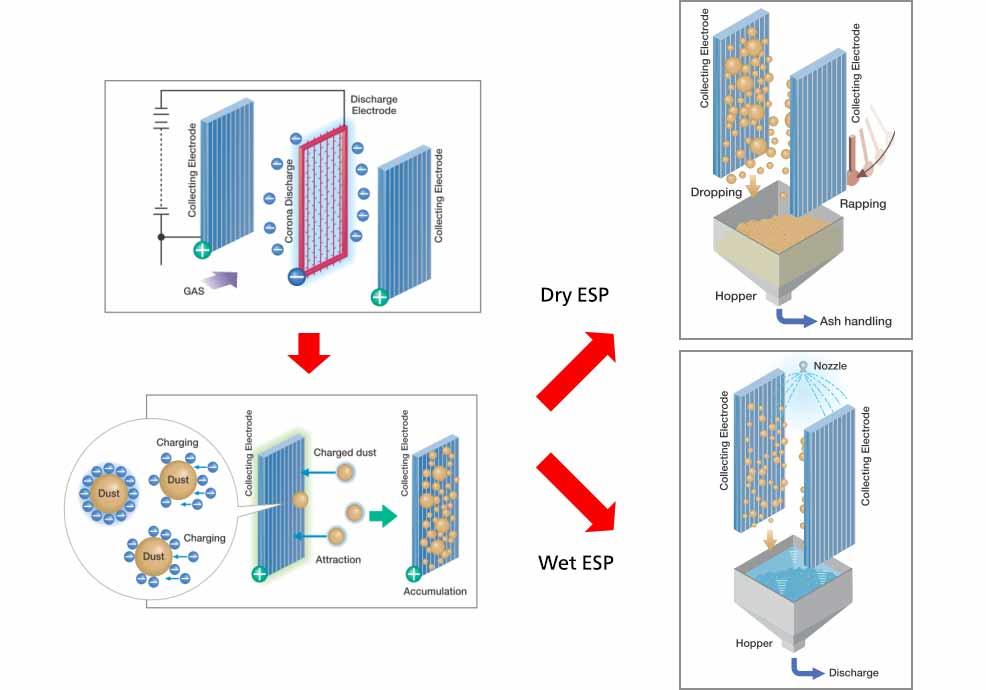
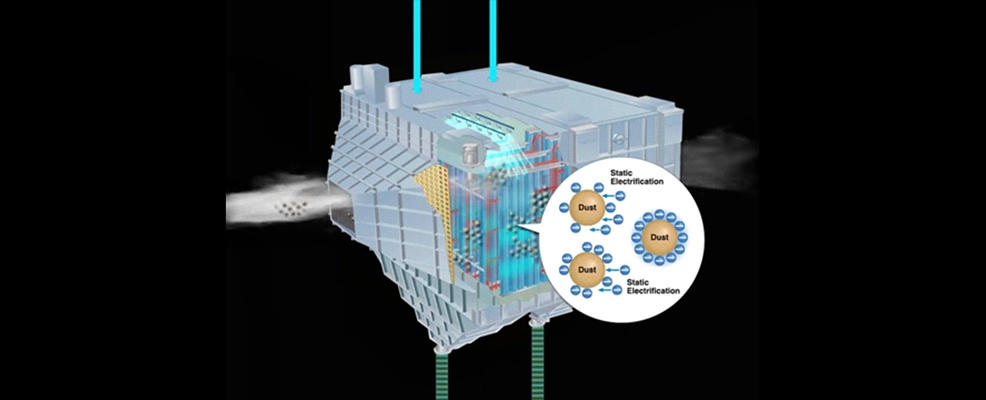
Basic principle of electrostatic precipitator
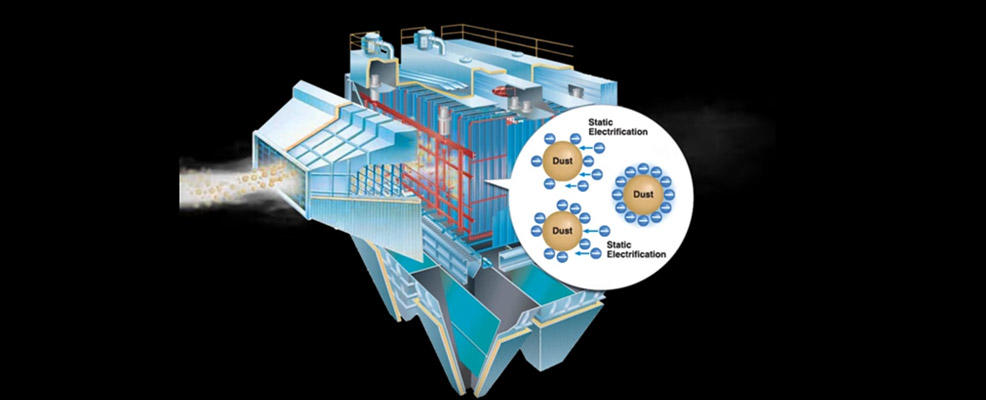
- When a high voltage is applied between the discharge electrode and the dust collecting electrode, ions are generated by corona discharge.
- Particles (dust) in gas that are charged by ions are attracted to the dust collecting electrode by electrostatic attraction and become accumulated.
- The accumulated dust are discharged into the hopper by hammering (dry method), brushing (dry method), or cleaning with spraying and flushing (wet method).
Dust collection performance and dust characteristics
-
In order to grasp the dust collection characteristics, we conduct preliminary surveys on various dust properties and gas conditions, as well as evaluations utilizing our extensive know-how, and then reflect the results in the basic plan.
-
Technologies for dust collection performance improvement measures (high-resistivity dust measure)
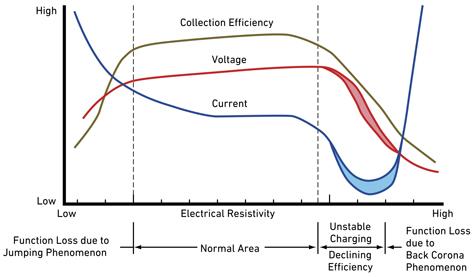
The biggest challenge for EPs for coal fired boilers is improving their performance against high electrical resistivity dust.
In the case of high electrical resistivity dust, there is a phenomenon called “inverse ionization,” which significantly reduces dust collection performance, and various measures have been taken based on research and elucidation of the phenomenon.
The table below shows the applicable technologies of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. We apply the optimal technologies depending on the application and situation to deliver high-performance and compact systems.
| Measure | Method | Technology |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Dust layer removal | Complete removal of dust | Moving electrode type (MEEP) |
| Wet type | ||
| (2) Reduction of electrical resistivity | Reduction in temperature | Low temperature EP system |
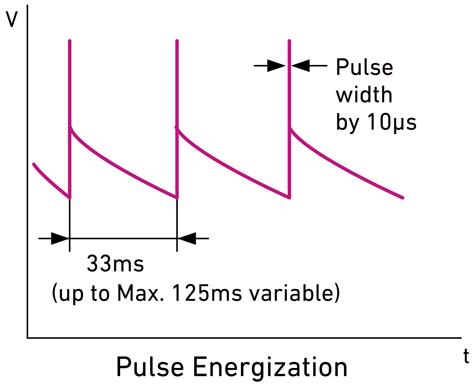
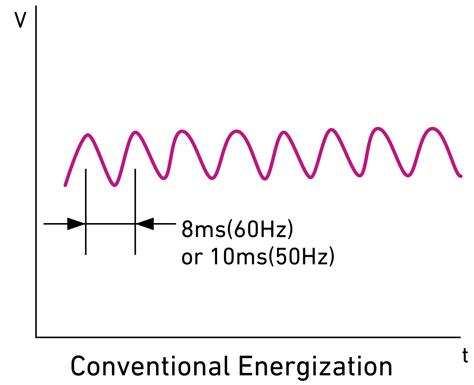
| (3) Current control | Charge control | Intermittent charging |
| pulse charging |
Dry type electrostatic precipitator
Dust collection and removal mechanism of the dust collecting electrode
There is a fixed electrode type and moving electrode type for removing the collected dust.
-
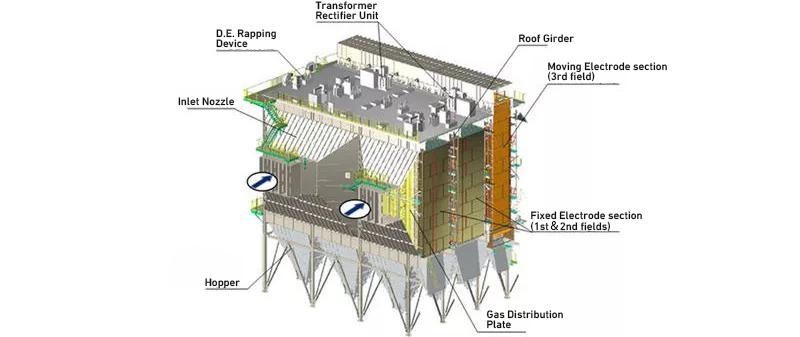
Fixed electrode type
Dust collected on the dust collecting plate are removed by the dust collecting electrode hammering device.
-
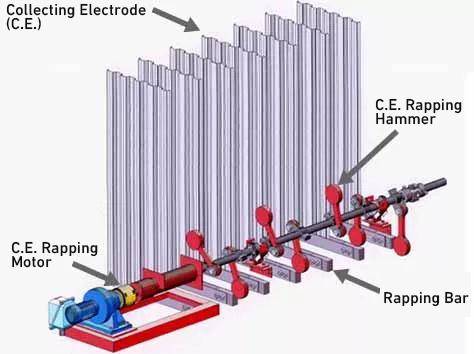
Fixed electrode type
-
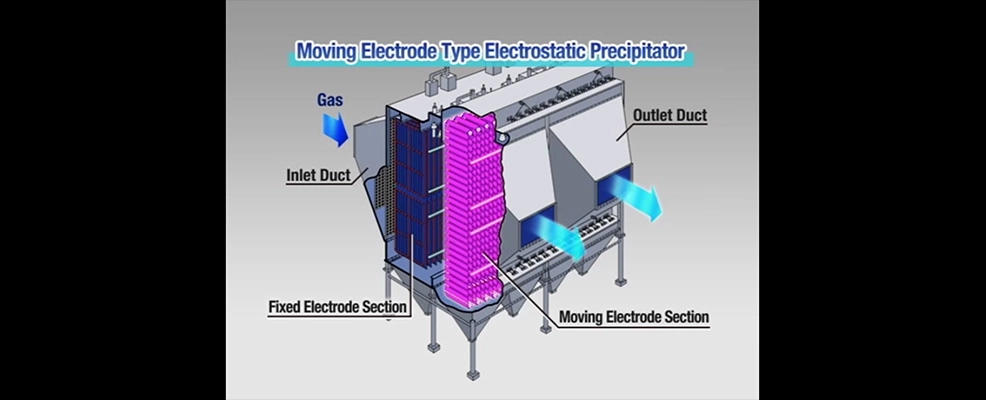
Moving electrode type
In the moving electrode system, the dust collecting plate is divided into strip-shaped elements and connected with chains to move the dust collecting electrode at low speed. Dust collected in the dust collection plate element are brushed off with a brush installed in the hopper.
-
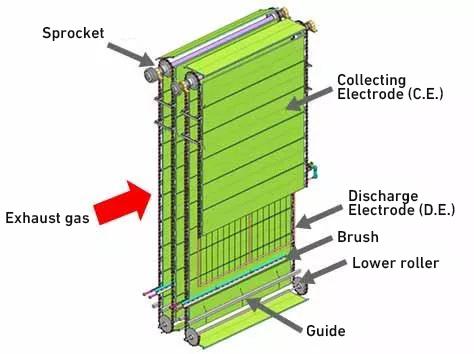
Moving electrode type
Structure of a fixed electrode type electrostatic precipitator
External structure
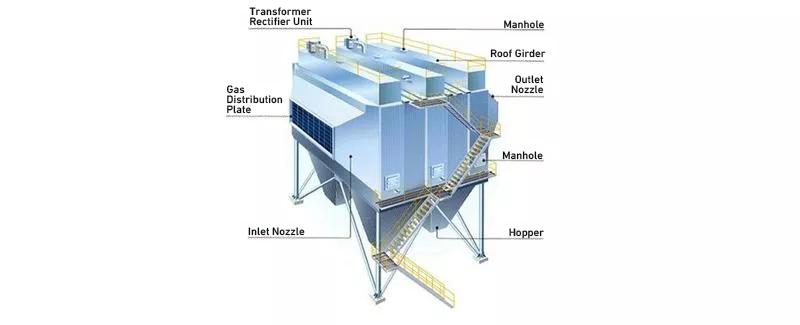
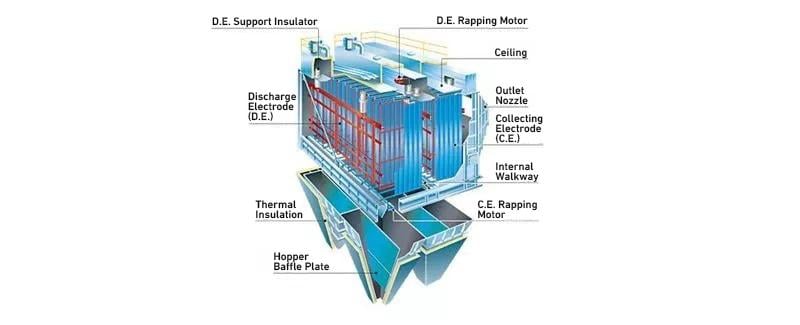
Internal structure
Video: Fixed electrode type electrostatic precipitator
Moving electrode type electrostatic precipitator "MEEP"
Effective collection of high resistivity dust
We developed a new method to remove the collected high electrical resistivity dust with a moving electrode structure and brush for the moving electrode type electrostatic precipitator "MEEP". At the same time, we also achieved miniaturization by improving the performance.
Structure of a moving electrode type electrostatic precipitator
Video: Moving electrode type electrostatic precipitator
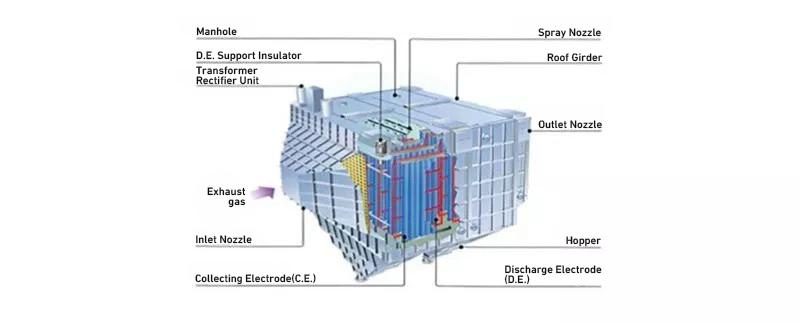
Wet type electrostatic precipitator
Features of wet type electrostatic precipitator
- Wet type electrostatic precipitators that use water to remove the collected dust exhibit high dust removal efficiency (up to 1 mg/m3N at the system outlet) without being affected by the electrical resistivity of the dust.
- It is suited to processes that require a very high degree of gas cleanliness and gases in conditions where dust collection is difficult with dry type electrostatic precipitators in terms of performance.
Internal structure
Introduction to the wet type electrostatic precipitator
Video: Wet type electrostatic precipitator
(Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Power Environmental Solutions, Ltd. Web Site
