Treatment Process

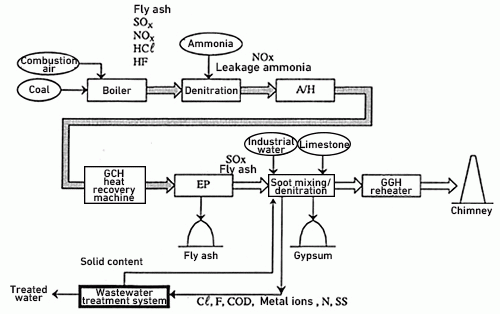
Configuration of the flue gas treatment system and wastewater components
Overall system configuration
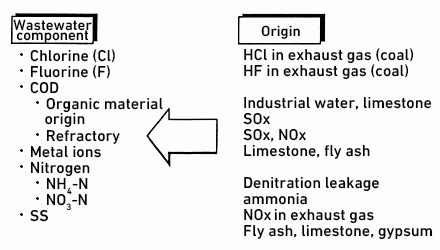
Origins of wastewater components
Desulfurization wastewater treatment block flow and features
Flow for soot separation
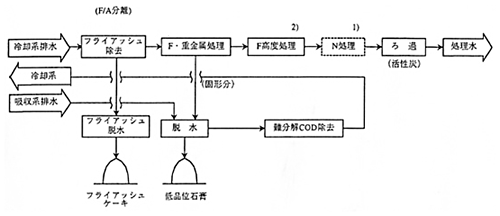
- 1When N regulation is applied
- 2When F regulation level is 10 mg/L or lower
Flow for soot mixing
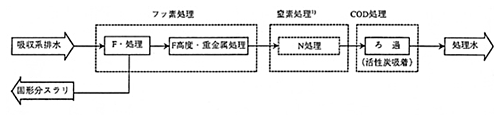
- 1When N regulation is applied
Fluorine treatment
Fluorine ion is adsorbed to aluminum hydroxide for sedimentation and decomposition with the use of an aluminum salt. A fluorine concentration of 10 mg/L or lower in treated water can be achieved by adopting the 2-stage flocculation-sedimentation method. Although calcium carbonate scaling occurred in the conventional process as sodium carbonate was added to the second stage of the flocculation-sedimentation tank, this disadvantage has been eliminated by combining an aluminum salt and chelating agent. Heavy metal ions are also removed with the addition of a chelating agent.
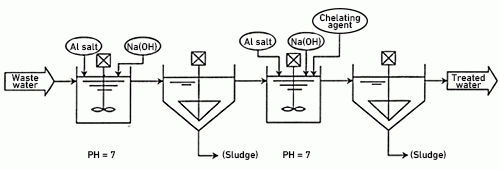
Features
- A fluorine concentration level of 10 mg/L or lower in treated water has been achieved with adoption of the 2-stage flocculation-sedimentation method
- Since treatment is conducted at pH 7, there is no need to adjust the pH of the treated water
Note) It is also possible to combine a fluorine adsorption resin in the process if the fluorine regulation level is even more strict.
Advanced treatment with fluorine adsorption resin
It is effective to treat with a fluorine adsorption resin if the fluorine regulation level is strict (< 8 mg/L).
The resin is regenerated when a certain amount of fluorine ions has been adsorbed.
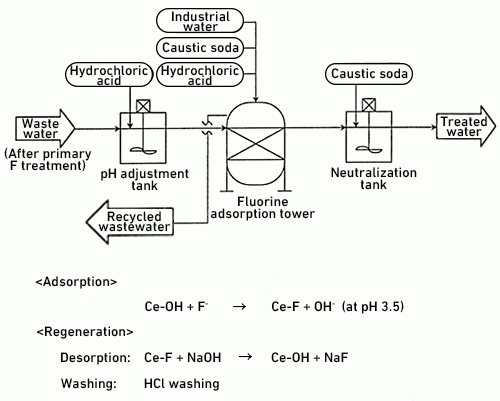
Features
- Capable of automatic operation and delivers stable treated water quality (no block management required)
- Compact layout (small installation area)
Nitrogen treatment
Nitrogen in wastewater consists of ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen, and it adopts the biological treatment method that most efficiently removes the nitrogen.
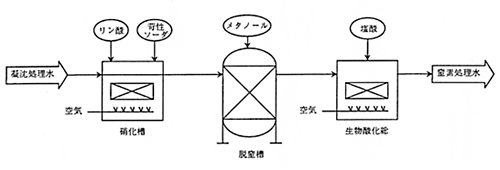
Features
- Stable treatment performance and causes no biological problems
- Easy to operate and does not require controlling sludge concentration, etc.
- Compact layout (small equipment footprint)
COD treatment
Causative substances subject to COD treatment include organic substances mixed from industrial water and limestone.
The amount of contamination depends on the industrial water quality and the properties of limestone.
Adsorption with activated carbon is an effective method for treating COD that is ascribed to organic substances.
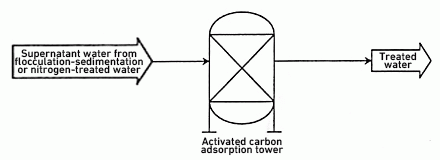
Features
- Simple equipment configuration
- Compact layout (small equipment footprint)
Products
- Electrostatic Precipitator
- Fabric filters
- Tunnel Electrostatic Precipitator
- Organic Solvent Exhaust Gas Treatment System
- Water Treatment
- Wastewater Treatment System
