Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) System
-
Maximum Capacity
1,050 MW
-
Max. NOx Removal Efficiency
95%
-
Low Environmental Impact
Slip NH3 < 2ppm
-
SCR Catalyst
High Reliability
High Durability
The selective catalytic reduction (SCR) removes nitrogen oxides (NOx) from flue gas emitted by power plant boilers and other combustion sources, and the catalyst is the key component of this system. Mitsubishi Power has compiled more than 40 years of experience in the supply of highly reliable SCR catalyst for its sophisticated flue gas treatment systems, contributing to the prevention of air pollution.
Special Features
We have supplied more than 1,400 SCR plants and catalyst units worldwide and have gained a larger market share with systems offering the following features:
- High NOx reduction meeting required emission standards for all kinds of fossil fuels
- Integrated NOx reduction linked with boilers/HRSGs
- Best optimization of catalysts for customers‘ requirements
- Multiple pollutant control to include mercury and low sulfur trioxide
- High reliability
- Long-term catalyst maintenance
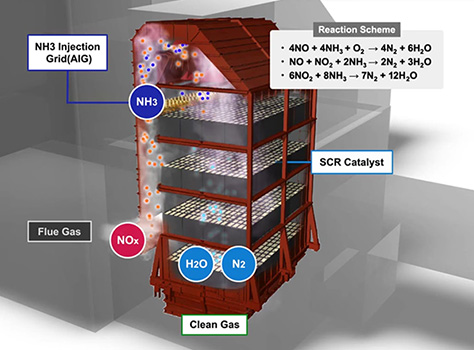
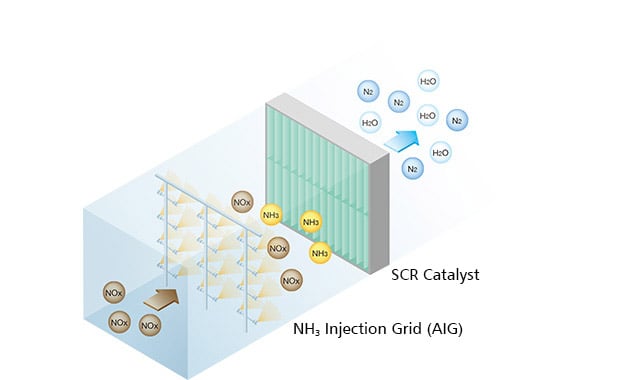
Basic Principle of NOx Reduction
The basic principle of SCR is simple. Ammonia is injected into the flue gas and NOx is decomposed into N2 and H2O vapor. The SCR catalyst efficiently facilitates ammonia and NOx reactions. The process forms no harmful by-products. Also plants using the SCR catalyst are easy to maintain and are capable of stable operation.
Chemical Reactions
- 4NO + 4NH3 + O2 → 4N2 + 6H2O
- 6NO2 + 8NH3 → 7N2 + 12H2O
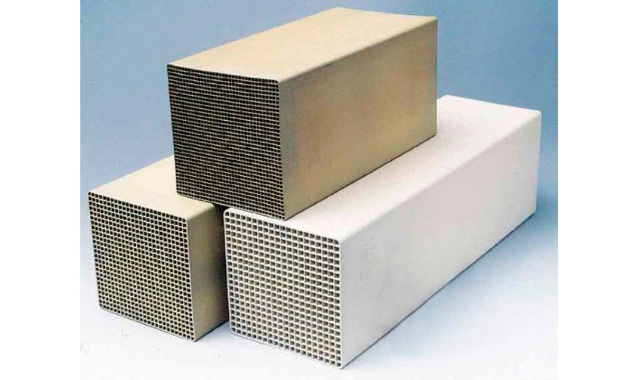
The SCR catalyst serves as the heart of the SCR system, and we provide both a plate-type catalyst and a honeycomb-type catalyst based on fuel type, system configuration, clients' needs, and other considerations.

Our SCR system has been applied to many types of boilers, HRSGs, and heaters that burn various fuels. We are one of the original developers of SCR systems and has over 40 years of experience, dating back to the 1970s.
Conventional Boiler Application
- Application Range
NOx Removal Efficiency: Max. 95%
Treated Gas Flow Rate : 3,140,000 Nm3/h, wet
Fuel : Coal, Oil, Gas, Residual Oil Fuel, etc.

Gas Turbine Simple Cycle (GTSC) Application
- Application Range
NOx Removal Efficiency: Max. 95%
Treated Gas Flow Rate: 1,560,000 Nm3/h, wet
Fuel : Gas, Oil
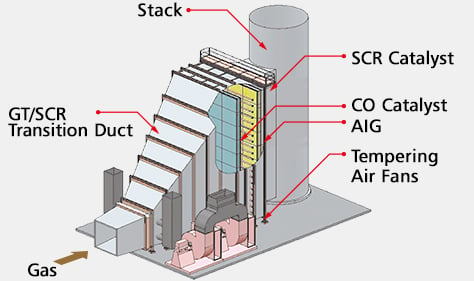
Gas Turbine Combined Cycle (GTCC) Application
- Application Range
NOx Removal Efficiency : Max. 95%
Treated Gas Flow Rate : 2,820,000 Nm3/h, wet
Fuel : Gas, Oil

Products
- GTCC
- Steam Power
- IGCC
- Geothermal
-
Gas Turbines
- Product Lineup
- Comparative Performance
-
Technical Information
- Gas Turbines for Mechanical Drive Applications
- Cutting-Edge Elemental Technology Producing 1600°C Class J Gas Turbines
- Development of High-Efficiency Gas Turbine Applying 1600°C Class J Technology
- Combustor Technologies Supporting Stable Operation
- Overview and Verification Status of T-Point 2 Demonstration Facility
- Comprehensive Efforts from Development to Manufacturing
- Summary of Orders
- Development History
- Product Selection Assistant (Middle & small Class)
- Aero-derivative Gas Turbines
- Steam Turbines
- Boilers
- Air Quality Control Systems (AQCS)
- Generators
-
Control Systems
- What is DIASYS?
- DIASYS Netmation
-
DIASYS Optional Products
- IR-S Infrared Flame Detector
- Net IR-S Infrared Flame Detector
- Rail Mounting Net IR-S
- Boiler Tube Leak Detector
- Shaft Vibration Analyzer
- Simulator
- Advanced Combustion Pressure Fluctuation Monitoring System (A-CPFM) / Combustion Pressure Fluctuation Monitoring System (CPFM)
- Multi-Coal Fired Boiler Optimum Control
- FXtoLS Adapter
- Fuel Cells
- Additive Manufacturing
- Catalogue
- HIACS Series
- Technical Report